Demystifying Price Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability and Pricing Strategy
Related Articles: Demystifying Price Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability and Pricing Strategy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Demystifying Price Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability and Pricing Strategy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying Price Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability and Pricing Strategy
In the competitive landscape of the modern marketplace, businesses constantly strive to achieve a delicate balance between profitability and customer satisfaction. One of the key levers in this equation is price markup, a critical aspect of pricing strategy that directly impacts a company’s financial health and market positioning. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear and informative understanding of price markup, exploring its nuances, importance, and practical implications for businesses across various industries.
Understanding Price Markup: The Foundation of Profitability
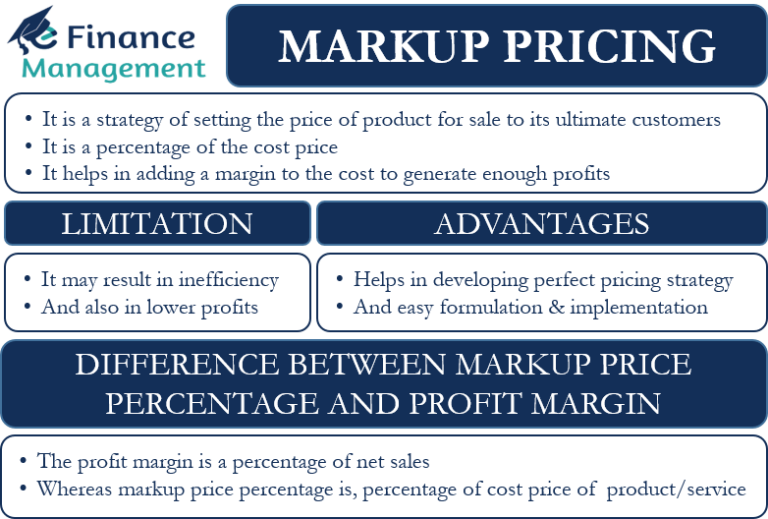
Price markup, in essence, represents the difference between a product’s cost and its selling price. It is the percentage added to the cost to determine the final price at which a product or service is offered to customers. This markup covers not just the direct costs associated with production or acquisition but also encompasses overhead expenses, profit margins, and a buffer for potential fluctuations in costs.
The Significance of Price Markup:
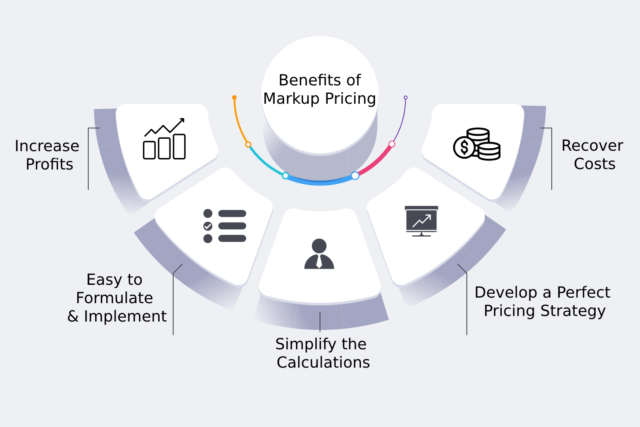
Price markup serves as a crucial tool for businesses to ensure financial viability and achieve their desired profit targets. By accurately calculating and implementing markup, companies can:
- Cover Operational Costs: Price markup allows businesses to cover all expenses associated with running the operation, including raw materials, labor, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative costs.
- Generate Profit: A well-defined markup strategy ensures that each sale contributes to the company’s overall profitability, enabling reinvestment, growth, and long-term sustainability.
- Maintain Competitive Pricing: While markup is essential for profitability, it also plays a role in maintaining competitive pricing. Businesses must strike a balance between ensuring sufficient markup to cover costs and profits and remaining competitive in the market.
- Adapt to Market Fluctuations: Price markup provides a buffer against potential fluctuations in input costs, allowing businesses to adjust pricing strategies without significantly impacting profit margins.
Factors Influencing Price Markup:
Several factors come into play when determining the appropriate price markup for a product or service. These factors can vary significantly across industries and even within individual businesses:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs associated with producing or acquiring a product, including raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead, form the foundation for calculating markup.
- Operating Expenses: These encompass all costs incurred in running the business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses.
- Desired Profit Margin: The profit margin represents the percentage of profit a company aims to achieve on each sale. This is a key driver of markup, as businesses strive to reach their targeted profitability levels.
- Competition: The competitive landscape plays a crucial role in determining price markup. Businesses must consider the pricing strategies of their competitors and adjust their markup accordingly to remain competitive.
- Market Demand: The demand for a product or service influences the potential price markup. High demand allows businesses to charge a higher markup, while low demand may necessitate lower markups to stimulate sales.
- Value Perception: Customers’ perception of the value of a product or service also influences the price markup. Businesses can leverage brand reputation, quality, and unique features to justify higher markups.
Types of Price Markup Calculations:
There are several common methods for calculating price markup, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: This method involves adding a fixed percentage markup to the cost of goods sold. It is a straightforward approach, but it can lead to inflexible pricing and may not reflect market realities.
- Value-Based Pricing: This method focuses on the perceived value of a product or service to the customer. It allows businesses to charge higher markups for products perceived as offering greater value, but it can be challenging to accurately assess customer value.
- Competitive Pricing: This method involves aligning pricing with competitors, aiming to stay competitive within the market. It can be effective in capturing market share but may not guarantee sufficient profitability.
- Dynamic Pricing: This method involves adjusting prices based on real-time market conditions, demand fluctuations, and competitor pricing. It offers flexibility and can optimize profitability but requires sophisticated data analysis and monitoring.
Implementing Price Markup Strategies:
Effective implementation of price markup strategies requires careful consideration and a systematic approach. Here are some key considerations:
- Conduct Thorough Cost Analysis: Accurately calculating the cost of goods sold and operating expenses is crucial for determining an appropriate markup.
- Define Profit Goals: Clearly define profit margin targets to guide pricing decisions and ensure that markup contributes to achieving these goals.
- Analyze Market Dynamics: Monitor competitor pricing, market trends, and customer demand to adapt pricing strategies and maintain competitiveness.
- Test and Optimize: Experiment with different markup levels and pricing strategies to identify the most effective approach for your business and target market.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Continuously monitor market conditions, competitor pricing, and cost fluctuations to adjust markup strategies as needed.
FAQs on Price Markup:
Q: What is the difference between markup and margin?
A: Markup is the percentage added to the cost of a product to determine its selling price. Margin, on the other hand, is the difference between the selling price and the cost of a product, expressed as a percentage of the selling price.
Q: How do I calculate markup percentage?
A: Markup percentage is calculated by dividing the markup amount (selling price – cost) by the cost of the product and multiplying by 100.
Q: How do I determine the right markup for my business?
A: The ideal markup varies significantly depending on factors such as industry, cost structure, competitive landscape, and desired profit margin. It is recommended to conduct a thorough cost analysis, consider market dynamics, and experiment with different markup levels to find the optimal balance for your business.
Q: Can I use different markup percentages for different products?
A: Yes, businesses often use different markup percentages for different products based on factors such as cost structure, demand, value perception, and competitive pressures.
Q: What are the potential risks of setting the markup too high or too low?
A: Setting the markup too high can lead to reduced sales and market share due to uncompetitive pricing. Conversely, setting the markup too low may not cover costs and lead to financial losses.
Tips for Optimizing Price Markup Strategies:
- Utilize Cost Accounting Tools: Employ cost accounting software or tools to track costs accurately and efficiently, providing a foundation for informed pricing decisions.
- Conduct Regular Market Research: Stay informed about competitor pricing, market trends, and customer preferences to adapt markup strategies and maintain competitiveness.
- Offer Value-Added Services: Enhance product offerings with value-added services, such as warranties, customer support, or personalized experiences, to justify higher markups.
- Consider Customer Segmentation: Implement different markup strategies for different customer segments based on their purchasing power, value perception, and loyalty.
- Embrace Dynamic Pricing: Utilize dynamic pricing strategies to adjust prices based on real-time market conditions, demand fluctuations, and competitor pricing.
Conclusion:
Price markup is an integral component of any successful pricing strategy, enabling businesses to ensure profitability, cover operational costs, and maintain competitiveness in the market. By understanding the factors influencing markup, employing appropriate calculation methods, and implementing strategic pricing strategies, businesses can effectively utilize price markup to achieve financial success and sustainable growth. Continuously monitoring market dynamics, adapting to changing conditions, and optimizing pricing strategies are essential for maximizing the benefits of price markup and achieving long-term profitability.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying Price Markup: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability and Pricing Strategy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!