The Power of Price Setting: Understanding the Price Maker in Today’s Economy
Related Articles: The Power of Price Setting: Understanding the Price Maker in Today’s Economy
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Price Setting: Understanding the Price Maker in Today’s Economy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Price Setting: Understanding the Price Maker in Today’s Economy
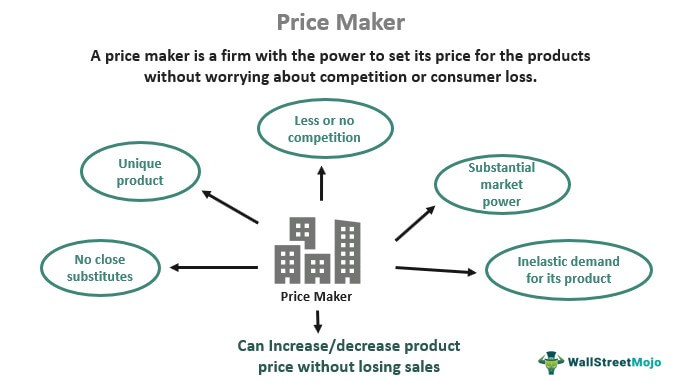
In the intricate dance of supply and demand, certain entities hold a unique power: the ability to influence, and even dictate, the price of goods and services. These entities are known as price makers, and their role is crucial in shaping the economic landscape.
This article delves into the concept of price makers, exploring their characteristics, the factors that enable them to set prices, and the implications of their actions on the market. We will also examine the benefits of price making for both the companies themselves and the broader economy.
Defining the Price Maker:
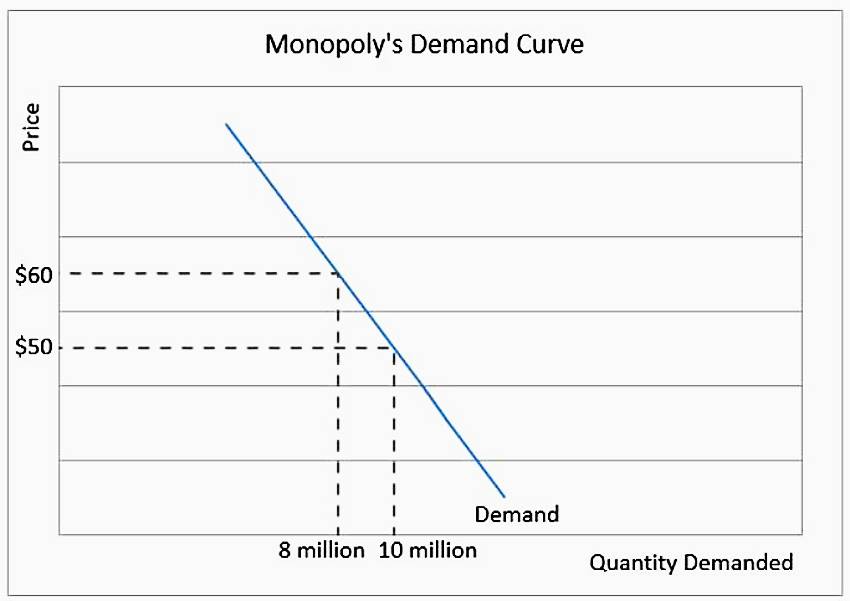
Unlike price takers, who must accept the prevailing market price, price makers possess the power to set prices above their marginal cost of production. This ability arises from several key factors:
- Market Dominance: Price makers typically hold a significant market share, giving them leverage over buyers. This dominance can stem from factors like economies of scale, strong brand recognition, or exclusive control over key resources.
- Differentiated Products: Price makers often offer unique or highly desirable products that are not easily substituted by competitors. This differentiation allows them to command a premium price.
- Limited Competition: The presence of few or weak competitors allows price makers to set prices without fear of immediate price wars or significant market share loss.
- High Barriers to Entry: Barriers to entry, such as high capital requirements, complex technology, or stringent regulations, deter new entrants and reinforce the market power of existing price makers.
Examples of Price Makers in Action:
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Pharmaceutical companies often hold patents on groundbreaking drugs, giving them significant market power to set high prices.
- Luxury Brands: Luxury brands rely on exclusivity and brand prestige to command premium prices for their products.
- Software Companies: Companies with dominant operating systems or software platforms can leverage their market power to set high prices for their products and services.
- Monopolies: In cases of true monopolies, where a single company controls the entire market, the price maker has complete control over pricing.
The Benefits of Price Making:
While often viewed with a critical eye, price making can offer several benefits:
- Innovation and Research: High profits generated through price making can be reinvested in research and development, leading to advancements in technology, medicine, and other fields.
- Investment and Growth: Price makers can attract significant capital investments, fostering economic growth and job creation.
- Quality Control: Price makers often have the resources and incentive to maintain high quality standards for their products and services.
- Consumer Choice: By offering differentiated products and services, price makers can cater to diverse consumer preferences and create more choices in the market.
The Potential Drawbacks of Price Making:
Despite its benefits, price making can also lead to negative consequences:
- Higher Prices for Consumers: Price makers can set prices higher than competitive market forces would dictate, leading to higher costs for consumers.
- Reduced Consumer Choice: The dominance of price makers can stifle competition and limit consumer choice, potentially leading to a lack of innovation and product variety.
- Inequality and Market Concentration: The power of price makers can contribute to economic inequality and market concentration, potentially leading to a less competitive and dynamic market.
FAQs about Price Makers:
Q: How do price makers determine their prices?
A: Price makers consider various factors when setting prices, including:
- Cost of production: This includes raw materials, labor, and other expenses.
- Demand elasticity: Price makers must consider how sensitive consumers are to price changes.
- Competition: The presence and pricing strategies of competitors play a role in determining the optimal price.
- Market conditions: Economic factors like inflation, interest rates, and consumer confidence can influence pricing decisions.
Q: Can price makers face challenges in setting prices?
A: Yes, price makers can face challenges in setting prices, including:
- Government regulation: Antitrust laws and consumer protection regulations can limit the pricing power of dominant firms.
- Consumer backlash: Consumers may react negatively to high prices, potentially leading to boycotts or reduced demand.
- Technological disruption: New technologies or entrants can disrupt existing markets and challenge the dominance of price makers.
Q: What are the ethical implications of price making?
A: The ethical implications of price making are complex and debated. Some argue that price makers have a responsibility to use their power responsibly and avoid exploiting consumers. Others argue that price making is a natural consequence of market forces and is necessary for innovation and economic growth.
Tips for Businesses in a Market with Price Makers:
- Focus on differentiation: Offer unique products or services that cater to specific customer needs and differentiate your offerings from those of price makers.
- Build strong relationships with customers: Cultivate loyalty by providing exceptional service and building trust.
- Embrace innovation: Invest in research and development to stay ahead of the competition and develop new products or services that can challenge price makers.
- Collaborate with other businesses: Form strategic alliances or partnerships to create economies of scale and enhance your competitive position.
Conclusion:
Price makers are a key feature of modern economies, wielding significant power to influence market dynamics. Their ability to set prices above marginal cost has both benefits and drawbacks, influencing innovation, economic growth, consumer welfare, and market competition. Understanding the nature and implications of price making is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike. By navigating the complexities of this power dynamic, stakeholders can strive for a balanced and sustainable market that benefits both producers and consumers.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Price Setting: Understanding the Price Maker in Today’s Economy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!